Tuberculosis of Hip-Osteoarticular Involvement



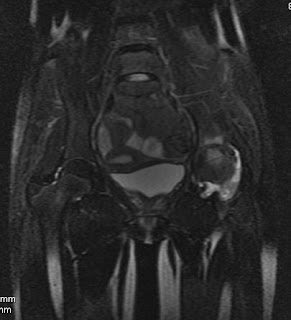
Findings-There is evidence of osseous destruction and altered marrow signal intensity involving the left hip, acetabulum & femoral head / neck appearing hypointense on T1WI and heterogeneously hyperintense on T2 / fat sat T2WI, there is evidence of synovial collection in relation to the left hip. Left hip joint space is reduced.
Opinion- Osseous destruction & marrow edema involving the bones forming the left hip articulation along with synovial collection & reduced joint space. Findings are consistent with infective etiology, likely tuberculosis. Clinical & laboratory collection is advised.
Dr.Sumer K Sethi, MD
Sr Consultant Radiologist ,VIMHANS and CEO-Teleradiology Providers
Tuberculosis of Hip-Osteoarticular Involvement
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, February 10, 2009
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, February 10, 2009
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, February 10, 2009
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, February 10, 2009
Rating:







No comments:
Post a Comment