Bilateral Ectopia Lentis in a case of Marfan Syndrome – An ultrasound diagnosis
Introduction –
Marfan syndrome is an inherited disorder that
affects connective tissue which supports and anchor body parts and organs
structures . It most commonly affects heart , eyes , blood vessels and sketelal
system.
There is no any unique sign and symptom of this disease but
constellation of long limbs, dislocation of lenses and aortic root dilation are
the key findings to make the diagnosis with confidence . Dr. Subhash Tailor , MD Bhilwara
[ Rajasthan ] is presenting a case
of Marfan syndrome whose ocular ultrasound revealed bilateral dislocation of
lens [Ectopic lentis].
Case report –
A 25 years old man attended my clinic for
ocular ultrasound , asked for decreased vision. His medical , clinical and genetic history was
notably suggesting a case of Marfan syndrome . Ocular USG was performed with a
voluson – 730 [ wipro GE ] system with 6 to 12 MHZ broad band linear probe . Examination
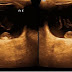
of his one eye revealed absence of crystalline lens at its position and it was
seen lodged posteriorly near retina as a well defined oval echogenic area [ see
figure ]. The second eye was also
attempted and revealed the same findings of dislocated lens , suggesting
bilateral ectopia lentis . The dislocation was typically supero-temporal . The
other ocular findings were obliterated
anterior chamber, some low level intragel internal echos indicating
degenerative changes and slightly increased axial
diameter of the eye balls . No retinal detachment was seen .
Discussion –
Marfan syndrome is a disorder of connective
tissue that holds the structures in position
in various parts of body . So weakness in the ligaments that holds the
lens in place causes subluxation and even complete dislocation of ocular
crystalline lens , called ectopia lentis . In this my case bilateral ectopia
lentis noted with subtle degenerative echos in the vitreous gel , and slightly increased axial diameter
of the eye balls . No evidence of
retinal detachment was found in either
eye . The dislocation of lens in Marfan
syndrome is classically superotemporal
whereas in similar condition Homocystinuria , the dislocation is infero nasal
type . In Marfan syndrome ectopia lentis noted in about 80% of cases.
The other ocular manifestations are glaucoma and
retinal detachment . The diagnosis of ectopia lentis in this case was straight
forward because of absence of lens at its normal position , and presence of the
cataractus [ small oval echogenic
structure ] lens dislocated and lodged posteriorly near retina in both eyes , suggesting
bilateral ectopia lentis in the light of
appropriate clinical settings.
Figure – Axial US images of both eye balls
showing a well defined oval echogenic structure posteriorly near retina , s/o
ectopia lentis . Some low level intragel
internal echoes also evident.
Bilateral Ectopia Lentis in a case of Marfan Syndrome – An ultrasound diagnosis
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, April 20, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, April 20, 2012
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, April 20, 2012
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, April 20, 2012
Rating:








1 comment:
Sir what are clinical finding in this patient of marfan syndrome.
Post a Comment