Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease -Teaching Points
50 year old male patient presented
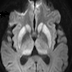
with classical triad of progressive dementia / myoclonus with EEG showing
periodic sharp waves. MRI suggest variant form of CJD (Creutzfeldt-Jacob
disease ) with posterior ( pulvinar ) and medial
thalami / periaqueductal gray matter / striatum / subtle involvement of the
neocortex showing restricted diffusion with reduced ADC values and T2/FLAIR
hyperintensities. Case submitted by: Dr.M.G.K.Murthy, Abdul Hamed, Bollinar narsimhulu
Teaching
points:-
Rare
Prion disease of slow virus variety.
Classical
triad as mentioned is seen only in 25% of the cases. Ataxia could represent
dominant feature. WHO suggest the diagnostic criteria of 14-3-3 in CSF, which
however is not easily available.
MRI
has emerged as possible diagnostic criterion of late. MRI is also expected to
suggest differentiating sporadic from the variant varieties.
Sporadic
shows corpus striatal / neocortex / posterior medial thalami restricted
diffusion along with T2/FLAIR hyperintensities.
The
variant variety suggest posterior ( Pulvinar ) and medial thalami / periaqueductal
gray matter / striatal involvement with less of neocortex involvement.
Pulvinar
sign is suggested when there is increased pulvinar signal as compared to the
anterior putamen. Hockey stick sign is suggested when there is additional
involvement of dorsomedial thalamic nuclei.
Pathology
of DW finding is accumulation of abnormal vacuoles in the cytoplasm and the
microvacuolation of neuritic processes heralding spongiform degeneration. Hyperintensities
in T2WI and PD correlate with spongiosis in basal ganglia structures, neuronal
loss and gliosis
Creutzfeldt-Jacob disease -Teaching Points
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, March 05, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, March 05, 2013
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, March 05, 2013
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Tuesday, March 05, 2013
Rating:











No comments:
Post a Comment