Solitary Pulmonary Nodule-CT
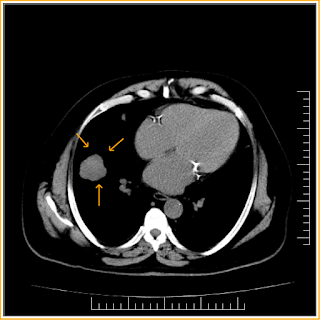
Incidentally detected lung nodule on CXR and followed up by CT, which shows lobulated outline lung nodule and mediastinal lymphnodes were also noted and biopsy was suggested for neoplastic etiology.
Teaching Points
1. A lung nodule has been defined by the
Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society as a rounded opacity, well or
poorly defined on a conventional radiograph, measuring up to 3 cm in diameter.
2. On computed tomography (CT) scan, a nodule
appears as a rounded or irregular opacity, well or poorly defined, measuring up
to 3 cm in diameter. Opacity less than 3
mm is defined as a micronodule.
3. Mimics of pulmonary nodules include
pseudonodules, which represent a rib fracture, a skin lesion, a device outside
the patient, anatomic variants, or composite areas of increased opacity.
4. The initial step after discovery of a SPN is to
determine its cause and characterize it as definitely benign, equivocal, or
definitely malignant on radiologic features.
5. Benign nodules include infectious granulomas and
hamartomas, whereas common malignant causes include primary lung cancer,
carcinoid tumors, and lung metastases.
6. Radiologic features, such as size, morphology,
and rate of growth, help to determine the likelihood of malignancy in a
majority of patients.
Solitary Pulmonary Nodule-CT
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Thursday, May 21, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Thursday, May 21, 2015
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Thursday, May 21, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Thursday, May 21, 2015
Rating:









No comments:
Post a Comment