Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: CT
Clinical data: 36 year old female with incidental focal hepatic lesion on USG
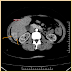
Focal 3.2 x 2.7cm lesion in the right lobe inferiorly which isoattenuating on plain images and shows enhancement in the arterial phase with a central less enhancing area and becomes isoattenuating in venous and delayed phase scan. This lesion causes a slight bulge in the hepatic surface. These findings, and age/sex of the patient and central hypoattenuating scar/arterial phase enhancement- leads to a differential of Focal nodular hyperplasia versus differentials. Clinical & Tc-Colloid Scan correlation suggested.
Teaching Points: FNH demonstrates bright arterial contrast enhancement except for the central scar which remains hypoattenuating. In the portal venous phase the lesion becomes isoattenuating to liver. The scar demonstrates enhancement on delayed scans in up to 80% of cases
Focal 3.2 x 2.7cm lesion in the right lobe inferiorly which isoattenuating on plain images and shows enhancement in the arterial phase with a central less enhancing area and becomes isoattenuating in venous and delayed phase scan. This lesion causes a slight bulge in the hepatic surface. These findings, and age/sex of the patient and central hypoattenuating scar/arterial phase enhancement- leads to a differential of Focal nodular hyperplasia versus differentials. Clinical & Tc-Colloid Scan correlation suggested.
Teaching Points: FNH demonstrates bright arterial contrast enhancement except for the central scar which remains hypoattenuating. In the portal venous phase the lesion becomes isoattenuating to liver. The scar demonstrates enhancement on delayed scans in up to 80% of cases
Focal Nodular Hyperplasia: CT
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, September 04, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, September 04, 2015
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, September 04, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, September 04, 2015
Rating:









No comments:
Post a Comment