Radiography - The less favoured learning Topic, Yet essential
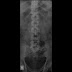
Image details: An artifact exclusive to digital radiography in the form of Ghosting is noted
Teaching points by Dr MGK Murthy
1.Three types of radiography exist in practice today, film screen variety (conventional) , Computed radiography (CR) using Photo Stimulable Phosphor plate (PSP ) and Digital radiography ( Using Amorphous thin film transistor(TFT) array coupled with phosphor layer of Cesium iodide(CSI) or Gadolinium oxysulfide.)
2. Additional Artifacts in DR systems are inherent to technology apart from the patient movement and other factors, as do exist in other varieties
3. Two types amongst them are important
(a) Image lag artifact (Ghosting artifact) due to DR design. Ghosting is inability to deactivate detector plate phosphor of the pervious image before the next latent image acquisition.
Latent image Signals in DR systems are readout at regular intervals by application of "Readout" voltage". However Not all of the trapped energy may be released by one readout and residual charge can be released during subsequent readouts of different exposures of next patient
This so called " trapped energy " produces a double exposure kind .
High opaque objects of the previous image would reappear as less dense components in the next image leading to Ghosting
This is usually avoided by delaying the next exposure to at least 60 seconds (can persist up to 15 minutes at times)
(b) Back scatter artifacts due to inadequate radiation shielding of detectors(mostly overcome by major manufactures by placing a thin lead film at the back of the detectors now)
4. Usually the factors of exposure need to be calibrated and displayed as chart in radiography room for all DR systems to avoid under or over exposures (General approximate rule is increase 15-20 KvP and 1/3 of mAs of conventional radiography systems). Standard charts are available from manufactures
5. Three main terms need to be understood for DR systems (a) Exposure index(EI) (b) Target Exposure index(EIt) (c) Deviation Index(DI)
Exposure index is a measure of radiation in relevant image region of the receptor (to be placed by ROI in the anatomical part of intended exposure like chest in chest in CXR and not upper abdomen)
Target Exposure index is reference exposure obtained when the image is optimally exposed(ideal for the select region)
Deviation index(DI) is the gap between the two calculated by formula and hence tells us whether exposure is optimal for image production (akin to olden days correct factors and hence readable image)(not for patient dose)
For example , DI of 1&3 indicate 26% and 100% overexposure and -1&-3 indicate 20%&50% underexposure
The exact quantifications of these 3 indices as indicated by world bodies like IEC (international electro technical commission) and AAPM (American association of Physicists in Medicine) is presently different and efforts on to find universal measurements independent of manufacturers
Radiography - The less favoured learning Topic, Yet essential
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, November 20, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, November 20, 2015
Rating:
 Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, November 20, 2015
Rating:
Reviewed by Sumer Sethi
on
Friday, November 20, 2015
Rating:









No comments:
Post a Comment